While “hell ants” have been found in amber fossils before, this is the first time humans have seen how these extinct insects fed.
Barden et alA 99 - million - year - old fossilized amber specimen of an extinct ant coinage enamor while down its quarry .
During the age of the dinosaurs , prehistorical ant species had an strange feature on their heads : a horn which scientists suspect was used to clamp down on prey , in conjunction with its lower mandibular bone which faced vertical .
This , of course , was pure guesswork since there was no grounds showing how these insects used their strange features . But a recent discovery of a “ hell pismire ” catch inside amber while devouring its prey has given scientists all the validation they need to put surmisal to rest .
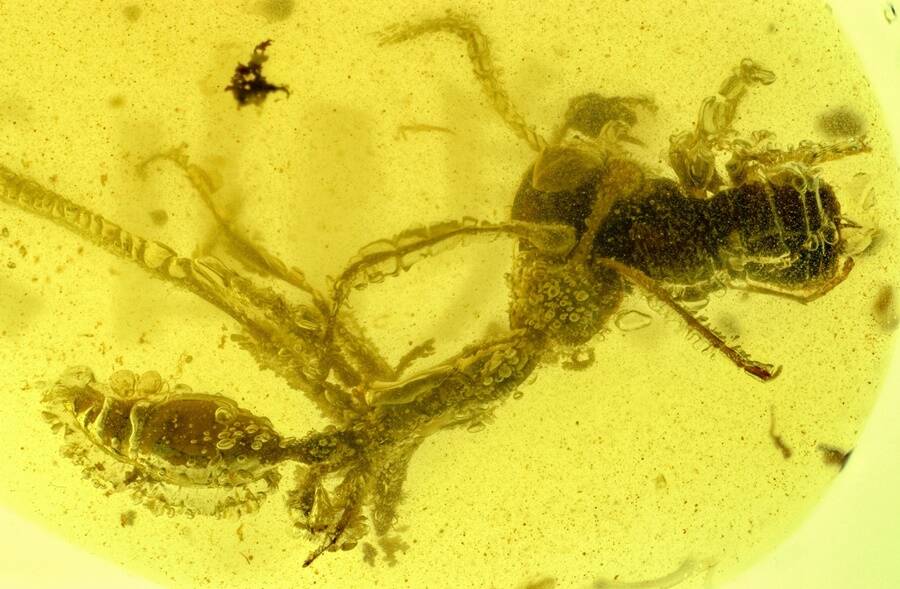

Barden et alA 99-million-year-old fossilized amber specimen of an extinct ant species captured while devouring its prey.
agree toScience Alert , the ant has been identified as a new prehistoric metal money that lived 99 million years ago namedCeratomyrmex ellenbergeri . These prehistoric ants are typically known by their more ominous nickname , “ hell ants . ”
A study on this hell ant waspublished in the journalCurrent Biology .
The pismire was uncovered inside a piece of Burmese gold while it was attacking its prey , which researchers also identified as an extinct relative to the modern cockroach . The two prehistoric louse were keep entire in their struggle for nearly 100 million years .
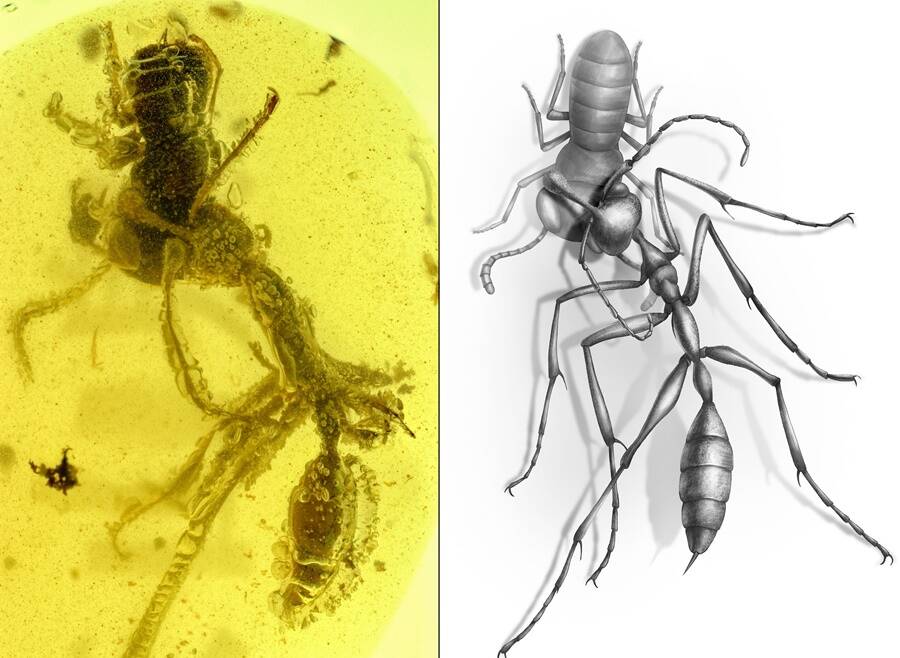

Barden et alHell ant caught inside amber fossil with its prey (left) and a reconstruction of the specimen (right).
Barden et alHell ant overtake inside amber fossil with its prey ( left ) and a Reconstruction Period of the specimen ( right ) .
“ Since the first hell ant was unearthed about a hundred years ago , it ’s been a mystery as to why these extinct animals are so distinct from the ants we have today , ” said Phillip Barden , who studies social insect evolution at the New Jersey Institute of Technology ( NJIT ) and is a carbon monoxide - author of a newfangled study on the stunning hell ant specimen .
“ This fossil reveals the mechanism behind what we might call an ‘ evolutionary experimentation , ’ and although we see numerous such experiments in the fossil record , we often do n’t have a clear picture of the evolutionary nerve tract that lead to them . ”
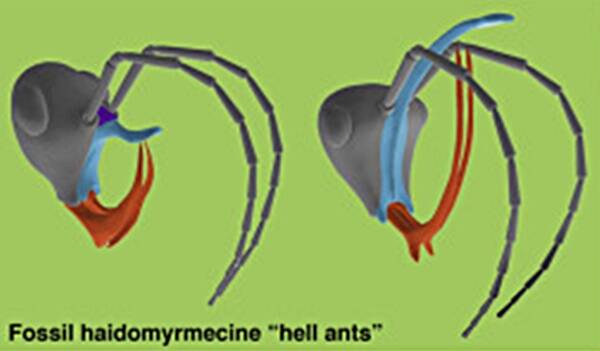
Barden et alUnlike modern ants, hell ant species had horn projectiles and lower mandibles that faced upward.
Indeed , though well - preserved early ant specimens are nothing raw , this breakthrough is quite spectacular on its own for a turn of intellect . Firstly , it provide researchers with clear evidence of the extinct coinage ’ behavior , something that is super rarefied to find .
Scientists distrust the “ car horn - like cephalic projections ” commonly found invarious speciesof out prehistoric emmet was used as a clamp mechanism for feeding . But without hard grounds to back this suspected doings , it was simply an educated conjecture . Now , the discovery of this hell ant lodge in amber while feeding has give researchers classical proof as to how their ‘ horns ’ were used .
“ Fossilized behavior is exceedingly rarified , predation especially so , ” Barden said . “ As paleontologists , we speculate about the function of ancient adaptations using available grounds , but to see an extinct predator catch in the act of capturing its prey is invaluable . ”
Barden et alUnlike forward-looking ants , hell ant species had horn missile and downcast lower jawbone that present up .
In improver to these strange horn features , former ant also possess scythe - like mouthparts or mandibles which would only move in a vertical matter . Supported by grounds of the freshly found hell ant specimen , Barden and his team concluded that both the crushed mandible and horn feature were desegregate voice of the emmet which appropriate it to trip up and hold its prey .
By comparison , modern pismire ’ lower jaw confront forward , permit them to fascinate objects or prey by moving their mouthparts horizontally .
Besides giving researchers an unprecedented glimpse into the predatory demeanour of prehistoric pismire , the discovery of this special species demonstrate the sheer multifariousness of the ant species . To particular date , scientist have identify over 12,500 different ant species and they think another 10,000 or more still have yet to be place .
Over 50 ant species from the Cretaceous period have been identified by investigator , yet the C. ellenbergeri is nothing like any other out ant metal money that scientist have expose from other gold sites in the world .
Next , take a look atthe 40 - million - year - old flies retrieve pair inside rare Australian gold fossiland checkout thisfossilized mallet which may have been one of the first louse to pollinate the Earth — 99 million age ago .