When you buy through links on our site , we may earn an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it works .
SAN FRANCISCO — Why are there so many birdcall about rainbows ?
Perhaps because there are so many dissimilar type , each with its own classifiable features , new research suggests .

A rare red rainbow lights up the sky in the Swiss Alps.
There are 12 types of rainbows , distinguished by various characteristic , the field of study suggest . Fat droplets of water or tiny sprays of mist will strike them , along with the angle of the sunlight . Rainbows can even come along astwins , triplets or quadruplet , Jean Ricard , a research worker at the National Meteorological Research Center , in France , said here yesterday ( Dec. 17 ) at the annual meeting of the American Geophysical Union .
And even a single rainbow is always changing , he said .
" They do n’t see likewise because when we look at a rainbow , one secondly by and by , the drop which forge the chief curtain call and the secondary bow are not the same , because they are falling , " Ricard said here in a news briefing . " If you see cautiously after a few minutes you will start to see some change in each rainbow . " [ Infographic : Earth ’s Atmosphere – Top to Bottom ]
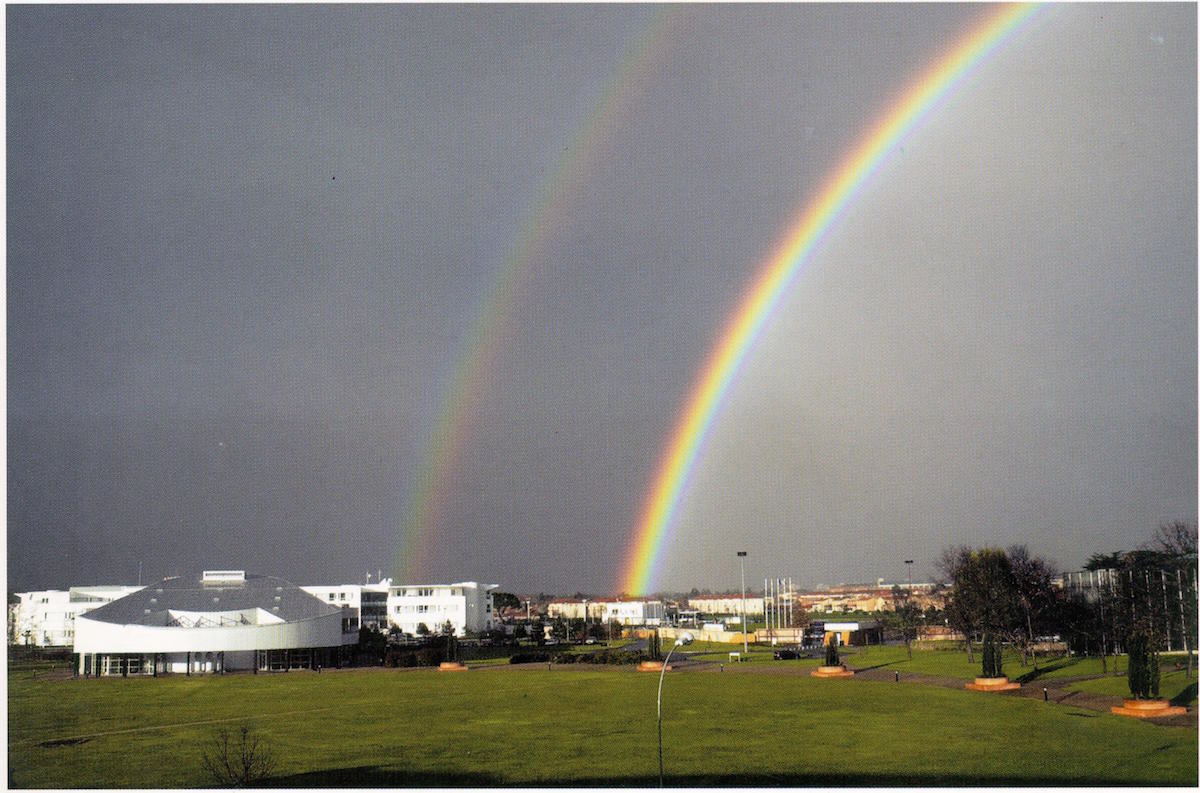

A double rainbow appeared in the summer sky above Toulouse following an afternoon storm.
categorization schema
Scientists have understood thebasics of rainbow formationsince at least Descartes ' meter : sun interacts with water droplets in the sky , and the light is both contemplate and refracted as it get into and leaves the raindrop . Because different wavelengths of light — which correspond to unlike colors — retard down by different speeds when they come to a raindrop , the different colors get bended at different angles , separating into the rainbow ’s distinctive chromaticity . ( The bizarre phenomenon roll in the hay as afire rainbowis neither a fire nor a rainbow , because it appears when light refract through ice crystals , not raindrops . )
In the past times scientists tried to classify rainbows ground on the colors in the rainbow , or the size of the droplet they refract through . But those classifications often overlook certain types of rainbows .

To capture all the innumerable " flavors " of rainbows , Ricard and his colleagues tried to figure out the minimum Seth of characteristics that would discover all rainbows . It grow out thatrainbowscan have up to four characteristic . There is the chief bow , with Red River on top and blue - trigger-happy on the bottom . Above that , petty reflections inside a rain droplet always form a lowly , fainter submit above the main bow , with the color invert . Between the two is a sinister region , called Alexander ’s striation , where minuscule light from the raindrops light reflects . And sometimes , there are additional bows , call supernumerary obeisance , which may occur when the light rays overspread and call off each other out via diffraction and interference in the atmosphere .
Types of rainbow
Based on those characteristics , they determined there are 12 different character ofrainbows , with inventive names like RB_1 , RB2 , etc . The rainbows change by whether all semblance are visible , whether they have a strong Alexander ’s band , and whether there are supernumerary bows . Some of the more striking rainbow include only red electric discharge , and then there are yellow-bellied - and - orange rainbow .

When Ricard and his colleagues analyze the physics , they found that the summit of the sun in the sky was the bighearted single gene affecting the rainbow ’s visual aspect . For instance , when the sun is very humiliated in the sky , such as at sunset , light is much less intense and must travel much farther to reach the eye . Only the red wavelength are able to make it through the atmosphere at this meter , he said
" At sunset or first light , the color of the Sunday and the intensity of the incoming luminosity changes dramatically , " Ricard said .
The size of the droplet also affected a rainbow ’s visual aspect , though to a less degree . Wider drop make for less lifelike rainbows with more wide spaced chromaticity , he say .

While rainbow research may seem more suitable to daydreamers and poets , it may have practical applications , Ricard said . For example , if scientists can spy rainbows onexoplanets , that may be a star sign of atmospheric piddle . And where there ’s water , there ’s often life .